Explore how SAP IoT connects devices, data, and SAP systems to enable predictive maintenance, automation, and smarter decisions.
SAP IoT is pivotal for SAP’s intelligent enterprise strategy. It connects the physical objects of the real world with business operations and helps organizations make informed decisions based not on guesswork but on what really happens. What is more, real-time data can serve as a wake-up call for enterprises when they want to prevent disruptions and optimize their work cycles for the long term.
Let’s Start With the Basics: What Is SAP IoT
SAP Internet of Things (IoT) is a set of capabilities that models real-world objects, such as robots and cars, and connects them to SAP systems. This way, you have an opportunity to securely integrate the latest data from your physical assets into your business workflows.
Historically, this functionality was a part of the SAP Leonardo IoT services, which is now a legacy solution. Nowadays, SAP IoT is not a single product but is delivered through SAP BTP and related solutions, such as SAP Asset Performance Management, Digital Twins, and integration services.
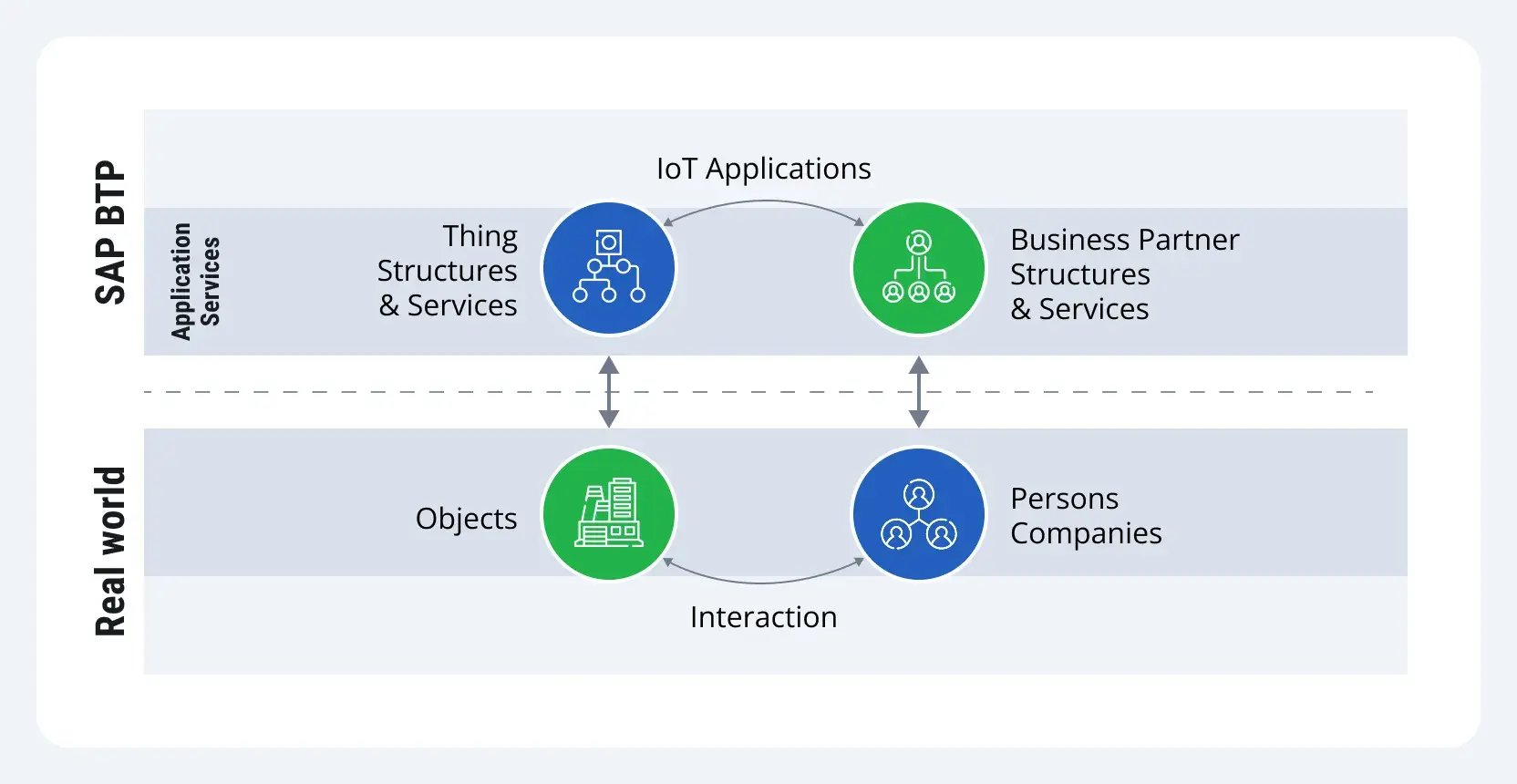
The Internet of Things SAP capabilities help organizations create a digital-twin-like environment with the representation of physical assets and persons or organizations that are involved in the activities related to those assets, such as production, monitoring, or distribution.
How It Works
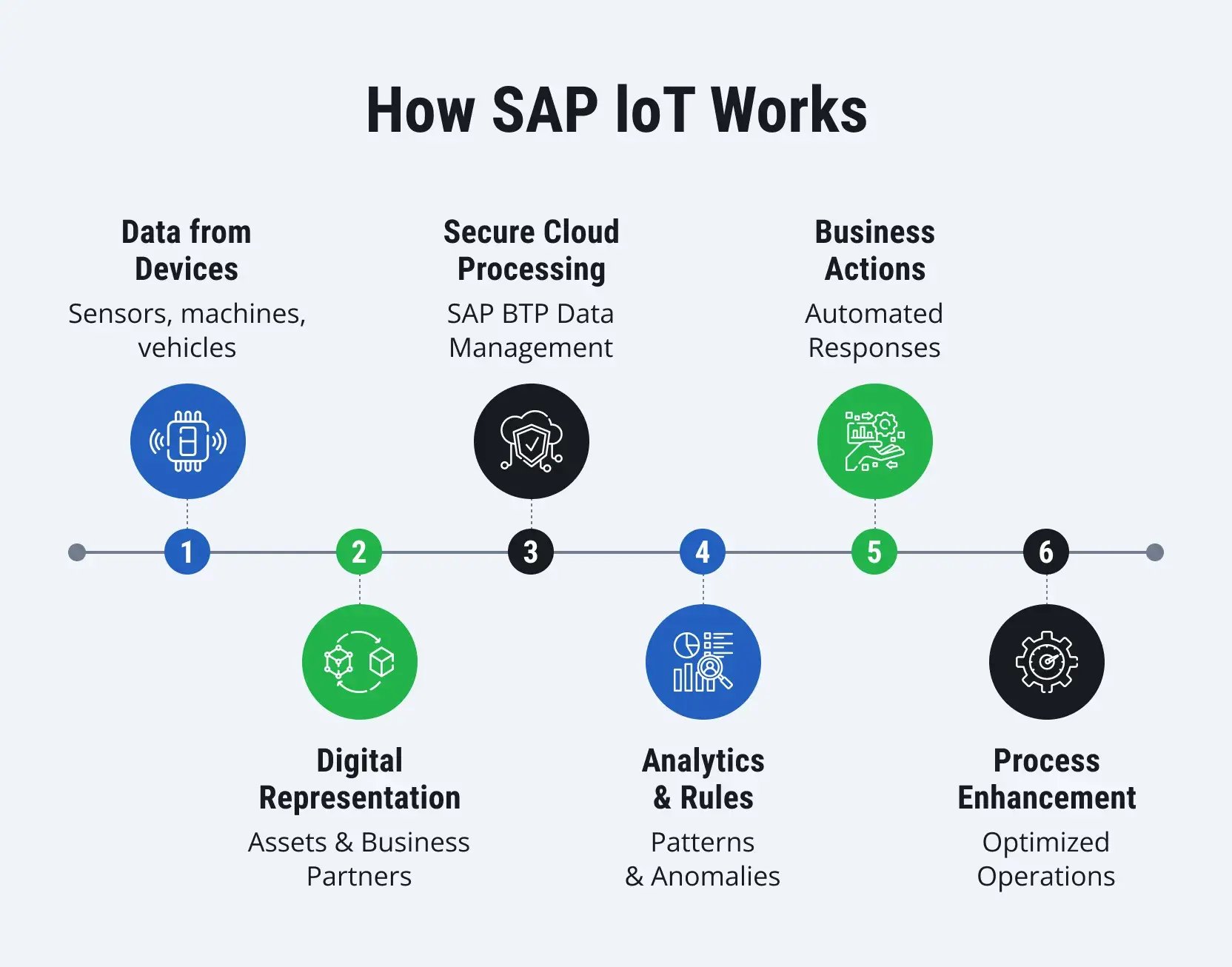
A typical SAP IoT workflow consists of six main steps.
1. Sensors and devices capture real-time data
Vehicles, machines, and other physical assets work and generate operational data such as heat levels or running hours. Sensors and IoT devices collect that data and also analyze the external conditions in which physical assets work. Depending on the industry, such indicators as humidity level or traffic congestion are read. It makes the work of physical assets visible for organizations in real time.
2. SAP IoT digitally models assets and stakeholders
With the help of cloud-based ingestion, the real-world data is processed and presented in digital models on SAP BTP, where:
- Physical assets are presented as Things.
- Stakeholders are marked as Business Partners.
- Changes with physical assets are defined as Events.
- Rules define business logic.
- Files store supporting documentation.
- Geolocation attributes location data to Things and Events.
- Authorization rules define the levels of access to the Things.
- Configurations define asset and process structures.
3. Analytics and rules interpret the context
SAP IoT rules are applied to asset behavior and external factors. Data ownership is governed through tenants on SAP BTP, and its sharing is controlled across Business Partners. These measures enable security and shared responsibility.
4. Meaningful situations are recognized
According to the interpreted context, SAP IoT identifies business risks (equipment failures, delays) and optimization opportunities, and creates a signal that an action needs to be performed.
5. SAP systems automatically respond
When a meaningful signal is detected, triggers in connected SAP systems are initiated so that an organization can start acting immediately. For example, a service request can be created and sent to a technician with suitable skills and a schedule.
6. Operations are improved
SAP IoT helps generate and use insights that optimize organizations’ operations in the long run. Companies can refine their strategies and shift from reactive to proactive management, using their physical assets in a more effective manner.
Turning Raw Signals Into Business Benefits
Adopting SAP IoT doesn’t mean organizations have to replace their traditional business world with a new one. They add something valuable to it instead:
- Minimization of unplanned downtime — with the help of predictive maintenance (now available within SAP APM), you can identify and address potential failures before they undermine your work.
- Reduction in maintenance costs and operating expenses — the implementation of SAP IoT allows you to avoid expensive emergency repairs and optimize maintenance planning.
- Cross-team visibility and coordination — the SAP IoT platform provides updates across all physical assets in different locations, and you can better coordinate your teams that work with the assets, which is especially important when conditions change.
- Informed choices — if you integrate SAP IoT with SAP digital core, your decisions will be based on actual performance telemetry and not a gut feeling.
- Room for scalable growth — building the foundation for handling assets on the basis of SAP BTP creates opportunities for enhancing and customizing IoT applications when an organization needs to implement new business models, services, and initiatives.
Examples in Action
Various industries and businesses can discover the new paradigm of obtaining and handling data with SAP IoT applications.
Logistics and transportation
Companies get access to location, vehicle state, and traffic updates, which help them organize routes, optimize schedules, and accelerate delivery.
Manufacturing
Organizations can rely on SAP IoT when monitoring the work of their equipment and preventing its unexpected failures. It’s also convenient to control the state of physical assets in remote and inaccessible areas, avoiding extra expenses.
Agriculture
SAP IoT provides environmental data that helps agricultural companies to decide on the most suitable time for planting or harvesting, automatically initiate soil treatment or irrigation, and apply other measures based on real conditions.
Public sector
Municipal authorities can transform urban management. By monitoring and analyzing environmental and traffic data, it’s possible to adjust the cycles of traffic lights, preventively maintain roads and bridges, and optimize garbage collection.
Integration With the SAP Landscape
You can discover the true value of SAP IoT when you connect it with other SAP systems in your organization. Scenarios can be the following:
- SAP S/4HANA: Responds to triggers from sensors and IoT devices in the format of alerts and other automated business transactions to initiate financial, service, or maintenance processes.
- SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM): Receives the data on machine status and performance from the shop floor and dynamically adjusts production schedules.
- SAP Business Network Asset Collaboration: Acts as a means for sharing IoT data with selected stakeholders so that they can plan their operations while the asset owner remains in full control over the data access.
- SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) and other SAP analytics solutions: Analyze and visualize contextualized IoT data for KPI tracking and decision making.
Navigating Implementation Challenges
When implementing SAP IoT, addressing organizational and technical aspects is the main best practice for proper work. Here is what SAP experts concentrate on.
Thought-out data integration strategy
SAP IoT doesn’t work in a vacuum; it needs a connection with your existing SAP systems and third-party solutions. Organizations should take care to have structured data models and interfaces to reuse data for the work of different departments and lines of business.
Security and scalability
Dealing with the Internet of Things usually means you will face large data volumes. To handle them, your digital architecture should meet certain security requirements and support the required level of scalability. It might sound cliché, but these are the prerequisites for any enterprise IoT system's survival.
Clear business objectives
You can receive enormous volumes of IoT data, but without predefined business use cases, you risk drowning in it. It’s crucial to decide whether you want to reduce downtime, optimize the usage of physical assets, or improve delivery before the actual rollout.
Governance and security measures
Working with IoT systems means a number of assets and stakeholders are involved in the processes. To avoid chaos and data breaches, SAP and IoT experts recommend establishing clear auditability, data authorization, and ownership, and taking care of cybersecurity measures.
Incremental approach
When you take your first steps in adopting SAP IoT or other IoT solutions, it’s highly recommended to implement them in a phased manner, starting from the most impactful use cases and adding more functionality over time. An incremental implementation in combination with ongoing monitoring and refinement will help you receive sustainable business results.
What To Expect in the Future
So, what about the future of SAP Internet of Things? While the situation is evolving rapidly, we can predict several trends based on the usage of operational data by organizations:
- AI-driven predictive analytics — the role of AI in processing and analyzing IoT data is growing, the predictions are getting more accurate, and recommendations are getting smarter.
- The spread of digital twins — organizations invest more in the digital representation of their assets to imitate various scenarios and optimize their operations without disrupting actual workflows.
- Sustainability focus — supporting sustainability goals remains the general trend for various organizations, and IoT technologies play a significant role in tracking critical metrics.
- Native ecosystem integration — IoT data insights are getting tightly embedded into digital enterprise ecosystems to support the work of other departments and navigate the general performance more confidently.
Moving Beyond Simple Connectivity
SAP IoT is an opportunity not only to connect several devices, but also a powerful driver of creating a digital infrastructure with efficient processes and decisions across your enterprise. It helps you stay on the safe side, eliminating unnecessary risks, and move forward faster, with operational excellence and innovation in mind.
IoT data is growing exponentially; therefore, SAP IoT apps can become a powerful tool for you to handle these streams and stay in the saddle.
What LeverX Can Do for You
We work with SAP IoT solutions, covering a range of services, to deliver measurable outcomes for organizations. Here is how we can be useful.
-
Architecture design and consulting
We assess your current structures, define how to model your physical assets and data sources on the SAP IoT level, reflecting and enhancing real operations.
-
IoT data integration
Our experts securely ingest data from IoT sensors, physical assets, and other external solutions with SAP IoT and the whole SAP ecosystem.
-
SAP IoT custom app development
LeverX builds tailored solutions on SAP BTP to support your specific processes, involving the usage of SAP IoT.
-
Predictive maintenance support
Our specialists configure asset monitoring, rules, and triggers, and help you prepare SAP IoT data for further analysis with the help of SAP analytics solutions; all this facilitates making proactive maintenance decisions.
-
Process optimization and automation with SAP IoT
We help you establish a connection between the latest IoT data and SAP systems to trigger actions needed for the alignment of the changes on the shop floor with execution and planning.
-
The full SAP IoT lifecycle support
The LeverX team undertakes SAP IoT implementation, support, and optimization to help you maintain SAP IoT applications modern, stable, and adjusted to your business strategy.
How useful was this article?
Thanks for your feedback!
.jpg)